Clients look to the expertise of our TUG ART ADVISORY worldwide to develop post-war, contemporary art and old masters collections for private residences, corporations, hotels, galleries and foundations with confidence and long term value. As art consultants we advise independently and fairly to find the art works that fit each collector's needs based on aesthetics with our highly valued relationships of trust and discretion.
We currently have art works from these artists for private client art sales.
We maintain a data base of established artists and emerging talent, but not all artists have been added to our list. can i
MODERN ARTISTS / POST MODERN ARTISTS
ALBERS, JOSEF
BASQUIAT, JEAN-MICHEL
BACON, FRANCIS

Josef Albers (/ˈælbərz, ˈɑːl-/; German: [ˈalbɐs]; March 19, 1888 – March 25, 1976)[1] was a German-born American artist and educator whose work, both in Europe and in the United States, formed the basis of some of the most influential and far-reaching art education programs of the twentieth century. Albers was born into a Roman Catholic family of craftsmen in Bottrop, Westphalia, Germany.[2] He worked from 1908 to 1913 as a schoolteacher in his home town; he also trained as an art teacher at Königliche Kunstschule in Berlin, Germany, from 1913 to 1915. From 1916 to 1919 he began his work as a printmaker at the Kunstgewerbschule in Essen. In 1918 he received his first public commission, Rosa mystica ora pro nobis, a stained-glass window for a church in Essen.[2] In 1919 he went to Munich, Germany, to study at the Königliche Bayerische Akademie der Bildenden Kunst, where he was a pupil of Max Doerner and Franz Stuck.[3]
BACON, FRANCIS
BASQUIAT, JEAN-MICHEL
BACON, FRANCIS

Francis Bacon (28 October 1909 – 28 April 1992) was an Irish-born British figurative painter known for his bold, grotesque, emotionally charged, raw imagery. He is best known for his depictions of popes, crucifixions and portraits of close friends. His abstracted figures are typically isolated in geometrical cage like spaces, set against flat, nondescript backgrounds. Bacon said that he saw images "in series", and his work typically focuses on a single subject for sustained periods, often in triptych or diptych formats. His output can be broadly described as sequences or variations on a single motif; beginning with the 1930s Picasso-informed Furies, moving on to the 1940s male heads isolated in rooms or geometric structures, the 1950s screaming popes, and the mid-to-late 1950s animals and lone figures, the 1960s portraits of friends, the nihilistic 1970s self-portraits, and the cooler more technical 1980s late works..
BASQUIAT, JEAN-MICHEL
BASQUIAT, JEAN-MICHEL
BASQUIAT, JEAN-MICHEL

Jean-Michel Basquiat (French: [ʒɑ̃ miʃɛl baskija]; December 22, 1960 – August 12, 1988) was an American artist.[1] Basquiat first achieved fame as part of SAMO©, an informal graffiti duo who wrote enigmatic epigrams in the cultural hotbed of the Lower East Side of Manhattanduring the late 1970s where the hip hop, post-punk, and street art movements had coalesced. By the 1980s, he was exhibiting his neo-expressionist paintings in galleries and museums internationally. The Whitney Museum of American Art held a retrospective of his art in 1992.Basquiat's art focused on "suggestive dichotomies", such as wealth versus poverty, integration versus segregation, and inner versus outer experience.[2] He appropriated poetry, drawing, and painting, and married text and image, abstraction, figuration, and historical information mixed with contemporary critique.[3]Basquiat used social commentary in his paintings as a "springboard to deeper truths about the individual",[2] as well as attacks on power structures and systems of racism, while his poetics were acutely political and direct in their criticism of colonialism and support for class struggle.[3] He died of a heroin overdose at his art studio at age 27.[4]
BEARD, PETER
CALDER, ALEXANDER
CALDER, ALEXANDER

Peter Hill Beard is an American artist, photographer, diarist and writer who lives and works in New York City and Kenya. His photographs of Africa, African animals and the journals that often integrate his photographs have been widely shown and published since the 1960s. Born in 1938 in New York City and raised in New York City, Alabama, and Islip, Long Island, Beard began keeping diaries as a young boy and making photographs, as an extension of the diaries, at the age of 12.[1] A graduate of Pomfret School, he entered Yale University in 1957, with the intention of pursuing pre-med studies, only to switch his major to art history. His mentors at Yale included Josef Albers, Richard Lindner and Vincent Scully.Inspired by earlier trips to Africa in both 1955 and 1960, Beard traveled to Kenya upon graduation. Working at Tsavo National Park, he photographed and documented the demise of 35,000 elephants and other wildlife, later to become the subject of his first book, “The End of the Game.”[2] During this time, Beard acquired Hog Ranch, a property near the Ngong Hillsadjacent to the coffee farm owned by Karen Blixen (Isak Dinesen), which would become his lifelong home-base in East Africa.[3]
CALDER, ALEXANDER
CALDER, ALEXANDER
CALDER, ALEXANDER

Alexander Calder (/ˈkɔːldər/; July 22, 1898 – November 11, 1976) was an American sculptor known as the originator of the mobile, a type of moving sculpture made with delicately balanced or suspended shapes that move in response to touch or air currents. Calder’s monumental stationary sculptures are called stabiles. He also produced wire figures, which are like drawings made in space, and notably a miniature circus work that was performed by the artist. Alexander "Sandy" Calder was born in 1898 in Lawnton, Pennsylvania.[2] His actual birthday, however, remains a source of much confusion. According to Calder's mother, Nanette (née Lederer), Calder was born on August 22, yet his birth certificate at Philadelphia City Hall, based on a hand-written ledger, stated July 22. When Calder's family learned about the birth certificate, they reasserted with certainty that city officials had made a mistake.Calder's grandfather, sculptor Alexander Milne Calder, was born in Scotland, immigrated to Philadelphia in 1868, and is best known for the colossal statue of William Penn on top of Philadelphia City Hall's tower. His father, Alexander Stirling Calder, was a well-known sculptor who created many public installations, a majority of them in nearby Philadelphia. Calder's mother was a professional portrait artist, who had studied at the Académie Julian and the Sorbonne in Paris from around 1888 until 1893. She moved to Philadelphia, where she met Stirling Calder while studying at the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts. Calder's parents married on February 22, 1895; his sister, Mrs. Margaret Calder Hayes, was instrumental in the development of the UC Berkeley Art Museum.[3]
CEZANNE, PAUL
CALDER, ALEXANDER
CHAGALL, MARC(1887-1985)

Paul Cézanne (US: /seɪˈzæn/ or UK: /sɪˈzæn/; French: [pɔl sezan]; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French artist and Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavor to a new and radically different world of art in the 20th century. Cézanne's often repetitive, exploratory brushstrokes are highly characteristic and clearly recognizable. He used planes of colour and small brushstrokes that build up to form complex fields. The paintings convey Cézanne's intense study of his subjects.Cézanne is said to have formed the bridge between late 19th-century Impressionism and the early 20th century's new line of artistic enquiry, Cubism. Both Matisse and Picasso are said to have remarked that Cézanne "is the father of us all."
CHAGALL, MARC(1887-1985)
CUCUEL, EDWARD(1875-1954)
CHAGALL, MARC(1887-1985)

Marc Zakharovich Chagall (/ʃəˈɡɑːl/ shə-GAHL;[3][nb 1] born Moishe Zakharovich Shagal;[4] 6 July [O.S. 24 June] 1887 – 28 March 1985) was a Russian-French artist of Belarusian Jewish origin.[1] An early modernist, he was associated with several major artistic styles and created works in virtually every artistic format, including painting, book illustrations, stained glass, stage sets, ceramic, tapestries and fine art prints.Art critic Robert Hughes referred to Chagall as "the quintessential Jewish artist of the twentieth century" (though Chagall saw his work as "not the dream of one people but of all humanity"). According to art historian Michael J. Lewis, Chagall was considered to be "the last survivor of the first generation of European modernists". For decades, he "had also been respected as the world's preeminent Jewish artist". Using the medium of stained glass, he produced windows for the cathedrals of Reims and Metz, windows for the UN, and the Jerusalem Windows in Israel. He also did large-scale paintings, including part of the ceiling of the Paris Opéra.Before World War I, he travelled between Saint Petersburg, Paris and Berlin. During this period he created his own mixture and style of modern art based on his idea of Eastern European Jewish folk culture. He spent the wartime years in Soviet Belarus, becoming one of the country's most distinguished artists and a member of the modernist avant-garde, founding the Vitebsk Arts College before leaving again for Paris in 1922.
CUCUEL, EDWARD(1875-1954)
CUCUEL, EDWARD(1875-1954)
CUCUEL, EDWARD(1875-1954)

Edward Cucuel (August 6, 1875, San Francisco – April 18, 1954, Pasadena, California), was an American-born painter who lived and worked in Germany. He was the son of a German newspaper publisher. At the age of fourteen he was already attending the San Francisco Art Institute and doing illustrations for The Examiner.[1] At the age of seventeen, he went to Paris where he attended the Académie Julian and the Académie Colarossi, finishing at the Académie des Beaux-Arts under Jean-Léon Gérôme.[2] When he came back to the United States in 1896, he briefly worked as a newspaper illustrator in New York, but returned to France and Italy to acquaint himself with the old masters at first hand. He ended up in Germany in 1899, where he worked as a free-lance newspaper illustrator in Berlin and Leipzig.
DUFY, RAOUL
CUCUEL, EDWARD(1875-1954)
CUCUEL, EDWARD(1875-1954)

Raoul Dufy (French: [ʁa.ul dy.fi]; 3 June 1877 – 23 March 1953) was a French Fauvist painter, brother of Jean Dufy. He developed a colorful, decorative style that became fashionable for designs of ceramics and textiles, as well as decorative schemes for public buildings. He is noted for scenes of open-air social events. He was also a draftsman, printmaker, book illustrator, scenic designer, a designer of furniture, and a planner of public spaces.
GOYA, FRANCISCO
GOYA, FRANCISCO
GOYA, FRANCISCO
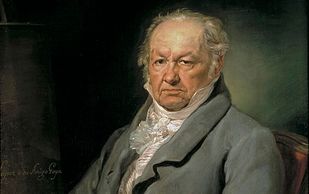
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes[A] (/ˈɡɔɪə/; Spanish: [fɾanˈθisko xoˈse ðe ˈɣoʝa i luˈθjentes]; 30 March 1746 – 16 April 1828) was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of late 18th and early 19th centuries and throughout his long career was a commentator and chronicler of his era. Immensely successful in his lifetime, Goya is often referred to as both the last of the Old Masters and the first of the moderns. He was also one of the great portraitists of modern times.[1]He was born to a modest family in 1746 in the village of Fuendetodos in Aragon. He studied painting from age 14 under José Luzán y Martinez and moved to Madrid to study with Anton Raphael Mengs. He married Josefa Bayeu in 1773; the couple's life together was characterised by an almost constant series of pregnancies and miscarriages. He became a court painter to the Spanish Crown in 1786 and this early portion of his career is marked by portraits of the Spanish aristocracy and royalty, and Rococo style tapestry cartoons designed for the royal palace.(Portrait of Goya by Vicente López Portaña)
GAUGUIN, PAUL
GOYA, FRANCISCO
GOYA, FRANCISCO

Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin (/ɡoʊˈɡæn/; French: [øʒɛn ɑ̃ʁi pɔl ɡoɡɛ̃]; 7 June 1848 – 8 May 1903) was a French post-Impressionist artist. Underappreciated until after his death, Gauguin is now recognized for his experimental use of color and Synthetist style that were distinctly different from Impressionism. His work was influential to the French avant-garde and many modern artists, such as Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse. Gauguin's art became popular after his death, partially from the efforts of art dealer Ambroise Vollard, who organized exhibitions of his work late in his career, as well as assisting in organizing two important posthumous exhibitions in Paris.[1][2] Many of his paintings were in the possession of Russian collector Sergei Shchukin[3] and other important collections.He was an important figure in the Symbolist movement as a painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer. His bold experimentation with color led directly to the Synthetist style of modern art, while his expression of the inherent meaning of the subjects in his paintings, under the influence of the cloisonnist style, paved the way to Primitivism and the return to the pastoral. He was also an influential proponent of wood engraving and woodcuts as art forms.[4][5]
HARING, KEITH
GOYA, FRANCISCO
HARING, KEITH

Keith Allen Haring (May 4, 1958 – February 16, 1990) was an American artist and social activist whose work responded to the New York City street culture of the 1980s by expressing concepts of birth, death, sexuality, and war.[2]Haring's work was often heavily political[3] and his imagery has become a widely recognized visual language of the 20th century.[4]
KAWS
KUSAMA, YAYOI
HARING, KEITH

Brian Donnelly (born 1974) – professionally known as Kaws (usually written KAWS) – is a pop artist and designer. His work includes repeated use of a cast of figurative characters and motifs, some dating back to the beginning of his career in the 1990s,[1] initially painted in 2D and later realised in 3D. Some of his characters are his own creation whilst others are reworked versions of existing icons. As he grew older, his influences came from traditional life painters, such as Gerhard Richter, Klaus Oldenberg, and Chuck Close.[2]He began as a graffiti artist, moving on to subvertising, and now makes sculpture, acrylic paintings on canvas and screen prints. He also collaborates commercially, predominantly on small edition toys (for example 2 or 8 inch tall figures), and also clothing, skate decks and other products.Kaws sculpture ranges in size from small to ten metres tall,[1] and are made from various materials including fibreglass, aluminium, wood and bronze.[3]His work is exhibited in galleries and museums, held in the permanent collections of public institutions, and avidly collected by individuals.[4] A number of books illustrating his work have been published. He lives and works in Brooklyn, New York.
KUSAMA, YAYOI
KUSAMA, YAYOI
KUSAMA, YAYOI

Yayoi Kusama (草間 彌生 or 弥生 Kusama Yayoi, born March 22, 1929) is a Japanese artist and writer. Throughout her career she has worked in a wide variety of media, including painting, collage, soft sculpture, performance art, and environmental installations, most of which exhibit her thematic interest in psychedelic colors, repetition, and pattern. A precursor of the pop art, minimalist and feminist art movements, Kusama influenced her contemporaries such as Andy Warhol, Claes Oldenburg, and George Segal and exhibited works alongside the likes of them.[1]In 1957, she moved to the United States, settling in New York City, where she produced a series of paintings influenced by abstract expressionism. Switching to sculpture and installation as her primary media, Kusama became a fixture of the New York avant-garde during the early 1960s when she became associated with the pop-art movement. Embracing the rise of the hippie counterculture of the late 1960s, Kusama came to public attention when she organized a series of happenings in which naked participants were painted with brightly colored polka dots. Although largely forgotten[citation needed] after departing the New York art scene in the early 1970s, Kusama is now acknowledged as one of the most important living artists to come out of Japan, and an important voice of the avant-garde.
LEGER, FERNAND
LICHTENSTEIN, ROY
LICHTENSTEIN, ROY

Joseph Fernand Henri Léger (French: [leʒe]; February 4, 1881 – August 17, 1955) was a French painter, sculptor, and filmmaker. In his early works he created a personal form of cubism which he gradually modified into a more figurative, populist style. His boldly simplified treatment of modern subject matter has caused him to be regarded as a forerunner of pop art.
LICHTENSTEIN, ROY
LICHTENSTEIN, ROY
LICHTENSTEIN, ROY

Roy Fox Lichtenstein (pronounced /ˈlɪktənˌstaɪn/; October 27, 1923 – September 29, 1997) was an American pop artist. During the 1960s, along with Andy Warhol, Jasper Johns, and James Rosenquist among others, he became a leading figure in the new art movement. His work defined the premise of pop art through parody.[2] Inspired by the comic strip, Lichtenstein produced precise compositions that documented while they parodied, often in a tongue-in-cheek manner. His work was influenced by popular advertising and the comic book style. He described pop art as "not 'American' painting but actually industrial painting".[3] His paintings were exhibited at the Leo Castelli Gallery in New York City.Whaam! and Drowning Girl are generally regarded as Lichtenstein's most famous works,[4][5][6] with Oh, Jeff...I Love You, Too...But...arguably third.[7] Drowning Girl, Whaam! and Look Mickey are regarded as his most influential works.[8] His most expensive piece is Masterpiece, which was sold for $165 million in January 2017.[9]
MARTIN, AGNES
LICHTENSTEIN, ROY
MARTIN, AGNES

Agnes Bernice Martin (March 22, 1912 – December 16, 2004), born in Canada, was an American abstract painter. Her work has been defined as an "essay in discretion on inward-ness and silence".[1] Although she is often considered or referred to as a minimalist, Martin considered herself an abstract expressionist.[2][3]She was awarded a National Medal of Arts from the National Endowment for the Arts in 1998.[4]
MATISSE, HENRI
MODIGLIANI, AMEDEO
MATISSE, HENRI

Henri-Émile-Benoît Matisse (French: [ɑ̃ʁi emil bənwɑ matis]; 31 December 1869 – 3 November 1954) was a French artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known primarily as a painter.[1]Matisse is commonly regarded, along with Pablo Picasso, as one of the artists who best helped to define the revolutionary developments in the visual arts throughout the opening decades of the twentieth century, responsible for significant developments in painting and sculpture.[2][3][4][5] Along with Picasso, Matisse helped to define and influence radical contemporary art in the 20th century. Although he was initially labelled a Fauve (wild beast), by the 1920s he was increasingly hailed as an upholder of the classical tradition in French painting.[6]His mastery of the expressive language of colour and drawing, displayed in a body of work spanning over a half-century, won him recognition as a leading figure in modern art.[7]
MIRÓ, JOAN
MODIGLIANI, AMEDEO
MATISSE, HENRI

Joan Miró i Ferrà (Catalan: [ʒuˈan miˈɾo]; 20 April 1893 – 25 December 1983) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, and ceramicist born in Barcelona. A museum dedicated to his work, the Fundació Joan Miró, was established in his native city of Barcelona in 1975, and another, the Fundació Pilar i Joan Miró, was established in his adoptive city of Palma de Mallorca in 1981.Earning international acclaim, his work has been interpreted as Surrealism, a sandbox for the subconscious mind, a re-creation of the childlike, and a manifestation of Catalan pride. In numerous interviews dating from the 1930s onwards, Miró expressed contempt for conventional painting methods as a way of supporting bourgeois society, and famously declared an "assassination of painting" in favour of upsetting the visual elements of established painting.[1]
MODIGLIANI, AMEDEO
MODIGLIANI, AMEDEO
MODIGLIANI, AMEDEO

Amedeo Clemente Modigliani (Italian pronunciation: [ameˈdɛːo modiʎˈʎaːni]; 12 July 1884 – 24 January 1920) was an Italian Jewish painter and sculptor who worked mainly in France. He is known for portraits and nudes in a modern style characterized by elongation of faces and figures, that were not received well during his lifetime, but later found acceptance. Modigliani spent his youth in Italy, where he studied the art of antiquity and the Renaissance until he moved to Paris in 1906. There he came into contact with prominent artists such as Pablo Picassoand Constantin Brâncuși.Modigliani's œuvre includes paintings and drawings. From 1909 to 1914, however, he devoted himself mainly to sculpture. His main subject was portraits and full figures of humans, both in the images and in the sculptures. During his life, Amedeo Modigliani had little success, but after his death he achieved greater popularity and his works of art achieved high prices. He died at age 35 in Paris of tubercular meningitis.
MONET, CLAUDE
PISSARRO, CAMILLE
MODIGLIANI, AMEDEO

Oscar-Claude Monet (/moʊˈneɪ/; French: [klod mɔnɛ]; 14 November 1840 – 5 December 1926) was a founder of French Impressionistpainting, and the most consistent and prolific practitioner of the movement's philosophy of expressing one's perceptions before nature, especially as applied to plein-air landscape painting.[1][2] The term "Impressionism" is derived from the title of his painting Impression, soleil levant (Impression, Sunrise), which was exhibited in 1874 in the first of the independent exhibitions mounted by Monet and his associates as an alternative to the Salon de Paris.Monet's ambition of documenting the French countryside led him to adopt a method of painting the same scene many times in order to capture the changing of light and the passing of the seasons. From 1883 Monet lived in Giverny, where he purchased a house and property and began a vast landscaping project which included lily ponds that would become the subjects of his best-known works. In 1899 he began painting the water lilies, first in vertical views with a Japanese bridge as a central feature, and later in the series of large-scale paintings that was to occupy him continuously for the next 20 years of his life.
PICASSO, PABLO
PISSARRO, CAMILLE
PISSARRO, CAMILLE

Pablo Picasso (/pɪˈkɑːsoʊ, -ˈkæsoʊ/;[2] Spanish: [ˈpaβlo piˈkaso]; 25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist, stage designer, poet and playwright who spent most of his adult life in France. Regarded as one of the most influential artists of the 20th century, he is known for co-founding the Cubist movement, the invention of constructed sculpture,[3][4] the co-invention of collage, and for the wide variety of styles that he helped develop and explore. Among his most famous works are the proto-Cubist Les Demoiselles d'Avignon (1907), and Guernica (1937), a dramatic portrayal of the bombing of Guernica by the German and Italian airforces.Picasso demonstrated extraordinary artistic talent in his early years, painting in a naturalistic manner through his childhood and adolescence. During the first decade of the 20th century, his style changed as he experimented with different theories, techniques, and ideas. After 1906, the Fauvist work of the slightly older artist Henri Matisse motivated Picasso to explore more radical styles, beginning a fruitful rivalry between the two artists, who subsequently were often paired by critics as the leaders of modern art.[5][6][7][8]Picasso's work is often categorized into periods. While the names of many of his later periods are debated, the most commonly accepted periods in his work are the Blue Period (1901–1904), the Rose Period (1904–1906), the African-influenced Period (1907–1909), Analytic Cubism (1909–1912), and Synthetic Cubism (1912–1919), also referred to as the Crystal period. Much of Picasso's work of the late 1910s and early 1920s is in a neoclassical style, and his work in the mid-1920s often has characteristics of Surrealism. His later work often combines elements of his earlier styles.Exceptionally prolific throughout the course of his long life, Picasso achieved universal renown and immense fortune for his revolutionary artistic accomplishments, and became one of the best-known figures in 20th-century art.
PISSARRO, CAMILLE
PISSARRO, CAMILLE
PISSARRO, CAMILLE

Camille Pissarro (French: [kamij pisaʁo]; 10 July 1830 – 13 November 1903) was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionistpainter born on the island of St Thomas (now in the US Virgin Islands, but then in the Danish West Indies). His importance resides in his contributions to both Impressionism and Post-Impressionism. Pissarro studied from great forerunners, including Gustave Courbet and Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot. He later studied and worked alongside Georges Seurat and Paul Signac when he took on the Neo-Impressionist style at the age of 54.In 1873 he helped establish a collective society of fifteen aspiring artists, becoming the "pivotal" figure in holding the group together and encouraging the other members. Art historian John Rewald called Pissarro the "dean of the Impressionist painters", not only because he was the oldest of the group, but also "by virtue of his wisdom and his balanced, kind, and warmhearted personality".[1] Cézanne said "he was a father for me. A man to consult and a little like the good Lord," and he was also one of Gauguin's masters. Renoir referred to his work as "revolutionary", through his artistic portrayals of the "common man", as Pissarro insisted on painting individuals in natural settings without "artifice or grandeur".Pissarro is the only artist to have shown his work at all eight Paris Impressionist exhibitions, from 1874 to 1886. He "acted as a father figure not only to the Impressionists" but to all four of the major Post-Impressionists, including Georges Seurat, Paul Cézanne, Vincent van Goghand Paul Gauguin.[2]
POLLOCK, JACKSON
RENOIR, PIERRE-AUGUSTE
RENOIR, PIERRE-AUGUSTE

Paul Jackson Pollock (January 28, 1912 – August 11, 1956), known professionally as Jackson Pollock, was an American painter and a major figure in the abstract expressionist movement. He was well known for his unique style of drip painting.During his lifetime, Pollock enjoyed considerable fame and notoriety; he was a major artist of his generation. Regarded as reclusive, he had a volatile personality, and struggled with alcoholism for most of his life. In 1945, he married the artist Lee Krasner, who became an important influence on his career and on his legacy.[4]Pollock died at the age of 44 in an alcohol-related single-car accident when he was driving. In December 1956, four months after his death, Pollock was given a memorial retrospective exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) in New York City. A larger, more comprehensive exhibition of his work was held there in 1967. In 1998 and 1999, his work was honored with large-scale retrospective exhibitions at MoMA and at The Tate in London.[5][6]
RENOIR, PIERRE-AUGUSTE
RENOIR, PIERRE-AUGUSTE
RENOIR, PIERRE-AUGUSTE

François Auguste René Rodin (12 November 1840 – 17 November 1917), known as Auguste Rodin (/oʊˈɡuːst roʊˈdæ̃/; French: [oɡyst ʁɔdɛ̃]), was a French sculptor. Although Rodin is generally considered the progenitor of modern sculpture,[1] he did not set out to rebel against the past. He was schooled traditionally, took a craftsman-like approach to his work, and desired academic recognition,[2] although he was never accepted into Paris's foremost school of art.Sculpturally, Rodin possessed a unique ability to model a complex, turbulent, deeply pocketed surface in clay. Many of his most notable sculptures were roundly criticized during his lifetime. They clashed with predominant figurative sculpture traditions, in which works were decorative, formulaic, or highly thematic. Rodin's most original work departed from traditional themes of mythology and allegory, modeled the human body with realism, and celebrated individual character and physicality. Rodin was sensitive to the controversy surrounding his work, but refused to change his style. Successive works brought increasing favor from the government and the artistic community.From the unexpected realism of his first major figure – inspired by his 1875 trip to Italy – to the unconventional memorials whose commissions he later sought, Rodin's reputation grew, such that he became the preeminent French sculptor of his time. By 1900, he was a world-renowned artist. Wealthy private clients sought Rodin's work after his World's Fair exhibit, and he kept company with a variety of high-profile intellectuals and artists. He married his lifelong companion, Rose Beuret, in the last year of both their lives. His sculptures suffered a decline in popularity after his death in 1917, but within a few decades, his legacy solidified. Rodin remains one of the few sculptors widely known outside the visual arts community.
ROTHKO, MARK
RENOIR, PIERRE-AUGUSTE
SHERMAN, CINDY

Mark Rothko (/ˈrɒθkoʊ/), born Markus Yakovlevich Rothkowitz (Russian: Ма́ркус Я́ковлевич Ротко́вич, Latvian: Markuss Rotkovičs; September 25, 1903 – February 25, 1970), was an American painter of Russian Jewish descent. Although Rothko himself refused to adhere to any art movement, he is generally identified as an abstract expressionist.
SHERMAN, CINDY
SOULAGES, PIERRE
SHERMAN, CINDY

Cynthia Morris "Cindy" Sherman (born January 19, 1954) is an American photographer and film director, best known for her conceptualportraits. In 1995, she was the recipient of a MacArthur Fellowship. Sherman has been criticized for her early Bus Riders series (1976–2000).[96] American Theatre critic Margo Jefferson has written, "[The African-American figures] all have nearly the same features, too, while Ms. Sherman is able to give the white characters she impersonates a real range of skin tones and facial features. This didn't look like irony to me. It looked like a stale visual myth that was still in good working order."[97]
SOULAGES, PIERRE
SOULAGES, PIERRE
SOULAGES, PIERRE

Pierre Soulages (French: [sulaʒ]; born 24 December 1919) is a French painter, engraver, and sculptor. In 2014 François Hollande described him as "the world's greatest living artist."[1]
Born in Rodez, Aveyron, in 1919, Soulages is also known as "the painter of black," owing to his interest in the colour "both as a colour and a non-colour. When light is reflected on black, it transforms and transmutes it. It opens a mental field all its own." He sees light as a work material; striations of the black surface of his paintings enable him to reflect light, allowing the black to come out of darkness and into brightness, thus becoming a luminous colour.Before World War II, Soulages already had toured museums in Paris seeking his vocation and after wartime military service, he opened a studio in Paris, holding his first exhibition at the Salon des Indépendants in 1947. He also worked as a designer of stage sets.In 1979, Pierre Soulages was made a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Letters.From 1987 to 1994, he produced 104 stained glass windows for the Romanesque Abbey church Sainte-Foy in Conques (Aveyron, France).Soulages is the first living artist invited to exhibit at the state Hermitage Museum of St. Petersburg and later with the Tretyakov Gallery of Moscow (2001).A composition he created in 1959 sold for 1.200.000 euros at Sotheby's in 2006.
STELLA, FRANK
SOULAGES, PIERRE
SOULAGES, PIERRE

Frank Philip Stella (born May 12, 1936) is an American painter, sculptor and printmaker, noted for his work in the areas of minimalism and post-painterly abstraction. Stella lives and works in New York City. Frank Stella was born in Malden, Massachusetts,[1] to parents of Italian descent. His father was a gynecologist, and his mother was an artistically inclined housewife who attended a fashion school and later took up landscape painting.[2]After attending high school at Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts, where he learned about abstract modernists Josef Albers and Hans Hofmann,[3] he attended Princeton University, where he majored in history and met Darby Bannard and Michael Fried. Early visits to New York art galleries fostered his artistic development, and his work was influenced by the abstract expressionism of Jackson Pollock and Franz Kline. Stella moved to New York in 1958, after his graduation. He is one of the most well-regarded postwar American painters still working today.[citation needed] He is heralded for creating abstract paintings that bear no pictorial illusions or psychological or metaphysical references in twentieth-century painting.[4]As of 2015, Stella lives in Greenwich Village and keeps an office there but commutes on weekdays to his studio in Rock Tavern, New York.[2]
TWOMBLY, CY
Van Gogh, VINCENT(1853-1890)
Van Gogh, VINCENT(1853-1890)

Edwin Parker "Cy" Twombly Jr. (/saɪ ˈtwɒmbli/; April 25, 1928 – July 5, 2011[1]) was an American painter, sculptor and photographer. He belonged to the generation of Robert Rauschenberg and Jasper Johns but chose to live in Italy after 1957.His paintings are predominantly large-scale, freely-scribbled, calligraphic and graffiti-like works on solid fields of mostly gray, tan, or off-white colors. Many of his works are in the permanent collections of most of the museums of modern art around the world, including the Menil Collection in Houston, the Tate Modern in London and the New York's Museum of Modern Art. He was also commissioned for the ceiling of a room of the Musée du Louvre in Paris.Many of his later paintings and works on paper shifted toward "romantic symbolism", and their titles can be interpreted visually through shapes and forms and words. Twombly often quoted the poets as Stéphane Mallarmé, Rainer Maria Rilke and John Keats, as well as many classical myths and allegories in his works. Examples of this are his Apollo and The Artist and a series of eight drawings consisting solely of inscriptions of the word "VIRGIL". In a 1994 retrospective, curator Kirk Varnedoe described Twombly's work as "influential among artists, discomfiting to many critics and truculently difficult not just for a broad public, but for sophisticated initiates of postwar art as well."[2] After acquiring Twombly's Three Studies from the Temeraire (1998–99), the Director of the Art Gallery of New South Wales said, "Sometimes people need a little bit of help in recognising a great work of art that might be a bit unfamiliar."[3] Twombly is said to have influenced younger artists such as Jean-Michel Basquiat, Anselm Kiefer, Francesco Clemente, and Julian Schnabel.[4]
Van Gogh, VINCENT(1853-1890)
Van Gogh, VINCENT(1853-1890)
Van Gogh, VINCENT(1853-1890)

Vincent Willem van Gogh (Dutch: [ˈvɪnsɛnt ˈʋɪləm vɑn ˈɣɔx] ( listen);[note 1] 30 March 1853 – 29 July 1890) was a Dutch Post-Impressionistpainter who is among the most famous and influential figures in the history of Western art. In just over a decade he created about 2,100 artworks, including around 860 oil paintings, most of them in the last two years of his life. They include landscapes, still lifes, portraits and self-portraits, and are characterised by bold colours and dramatic, impulsive and expressive brushwork that contributed to the foundations of modern art. His suicide at 37 followed years of mental illness and poverty.Born into an upper-middle-class family, Van Gogh drew as a child and was serious, quiet and thoughtful. As a young man he worked as an art dealer, often travelling, but became depressed after he was transferred to London. He turned to religion, and spent time as a Protestantmissionary in southern Belgium. He drifted in ill health and solitude before taking up painting in 1881, having moved back home with his parents. His younger brother Theo supported him financially, and the two kept up a long correspondence by letter. His early works, mostly still lifes and depictions of peasant labourers, contain few signs of the vivid colour that distinguished his later work. In 1886, he moved to Paris, where he met members of the avant-garde, including Émile Bernard and Paul Gauguin, who were reacting against the Impressionistsensibility. As his work developed he created a new approach to still lifes and local landscapes. His paintings grew brighter in colour as he developed a style that became fully realised during his stay in Arles in the south of France in 1888. During this period he broadened his subject matter to include olive trees, cypresses, wheat fields and sunflowers.
VUILLARD
Van Gogh, VINCENT(1853-1890)
VUILLARD

Jean-Édouard Vuillard (French: [vɥijaʁ]; 11 November 1868 – 21 June 1940) was a French painter and printmaker associated with the Nabis.[1]
Jean-Édouard Vuillard was born on 11 November 1868 in Cuiseaux (Saône-et-Loire),[2] where he spent his youth; in 1878
his family moved to Paris.[3] Vuillard's father, a retired army captain, was 27 years older than his mother Marie Vuillard (née Michaud).[4] After his father's death in 1884, Vuillard received a scholarship to continue his education. In the Lycée Condorcet[5] Vuillard met Ker Xavier Roussel[6] (also a future painter and Vuillard's future brother in law), Maurice Denis, musician Pierre Hermant, writer Pierre Véber, and Lugné-Poe.
In 1885, Vuillard left the Lycée Condorcet. On the advice of his closest friend, Roussel, he refused a military career and joined Roussel at the studio of painter Diogène Maillart. There, Roussel and Vuillard received the rudiments of artistic training. From 1886 to 1888, he studied at the Académie Julian.[7][8] In 1887, after three unsuccessful attempts, Vuillard passed the entrance examination for the École des Beaux-Arts.[9] Vuillard kept a private journal from 1888–1905 and later from 1907–1940.
WARHOL, ANDY

Andy Warhol (/ˈwɔːrhɒl/;[1] born Andrew Warhola; August 6, 1928 – February 22, 1987) was an American artist, director and producer who was a leading figure in the visual art movement known as pop art. His works explore the relationship between artistic expression, celebrity culture, and advertising that flourished by the 1960s, and span a variety of media, including painting, silkscreening, photography, film, and sculpture. Some of his best known works include the silkscreen paintings Campbell's Soup Cans (1962) and Marilyn Diptych (1962), the experimental film Chelsea Girls (1966), and the multimedia events known as the Exploding Plastic Inevitable (1966–67).Born and raised in Pittsburgh, Warhol initially pursued a successful career as a commercial illustrator. After exhibiting his work in several galleries in the late 1950s, he began to receive recognition as an influential and controversial artist. His New York studio, The Factory, became a well-known gathering place that brought together distinguished intellectuals, drag queens, playwrights, Bohemian street people, Hollywood celebrities, and wealthy patrons. He promoted a collection of personalities known as Warhol superstars, and is credited with coining the widely used expression "15 minutes of fame." In the late 1960s, he managed and produced the experimental rock band The Velvet Underground and founded Interview magazine. He authored numerous books, including The Philosophy of Andy Warhol and Popism: The Warhol Sixties. He is also notable as a gay man who lived openly as such before the gay liberation movement. After a gallbladdersurgery in 1987, Warhol died in February of that year at the age of 58.Warhol has been the subject of numerous retrospective exhibitions, books, and feature and documentary films. The Andy Warhol Museum in his native city of Pittsburgh, which holds an extensive permanent collection of art and archives, is the largest museum in the United States dedicated to a single artist. Many of his creations are very collectible and highly valuable. The highest price ever paid for a Warhol painting is US$105 million for a 1963 canvas titled Silver Car Crash (Double Disaster); his works include some of the most expensive paintings ever sold.[2] A 2009 article in The Economist described Warhol as the "bellwether of the art market".[3]
Copyright © 2018 Tug Art Advisory - All Rights Reserved.
All biographies are from Wikipedia